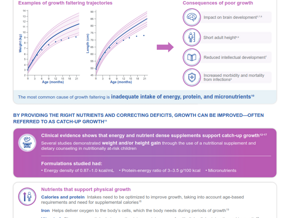
![[Literature Library] Human milk omega-3 fatty acid composition and infant temperament](/sites/default/files/styles/header_image_article_mobile/public/2020-02/056_Mother-breastfeeding-baby-opt.jpg.webp?itok=_7gzn-j7)
Article
[Literature Library] Human milk omega-3 fatty acid composition and infant temperament
Public health
2 min read
Link to Publication: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6949911/
Reference
Hahn-Holbrook J et al. Nutrients. 2019;11(12).
Other online materials that you might be interested in:
[Hot science] Omega-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids on cognitive performance and behavior in children
WYE-EM-031-FEB-20
If you liked this post you may also like