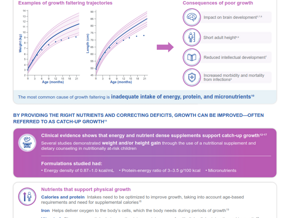
[Science Update] Recommendations for optimal prenatal supplementation for women in the US
Vitamin A
- Prenatal supplements with 1200 mcg of pre-formed vitamin A in the form of retinol, and 1000 mcg in the form of mixed carotenoids were recommended
Vitamin C
- Prenatal supplements with ~200 mg of vitamin C were recommended
Vitamin D
- Daily intake of ≥2000 – 4000 IU was recommended
- Measure serum vitamin D levels in the form of 25(OH)D, target at a level of ≥30 ng/mL—40 ng/mL
- Women with darker skin (Hispanic and especially Black) may require more
Vitamin E
- Prenatal supplements with ≥19 mg of vitamin E were recommended
- Synthetic forms of vitamin E should be avoided due to their little biological activity
- Vitamin E in ‘d’ forms from natural sources should be used
Vitamin K
- Prenatal supplements with ≥90 mcg of vitamin K were recommended
- For women with risk of preterm birth, high dose of vitamin K therapy (10 mg, possibly repeatedly) was recommended
- For women with previous bariatric surgery, weekly supplementation of 10 mg may be needed
Vitamin B1 (Thiamine)
- Prenatal supplements with ~6 mg of thiamine were recommended
Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin)
- Prenatal supplements with ~2 mg of riboflavin were recommended
- Daily supplementation of 2.5 mg may be needed for women with very poor diet
Vitamin B3 (Niacin)
- Prenatal supplements with ~35 mg niacin/day were recommended
Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic acid)
- Prenatal supplements with ~10 mg of pantothenic acid were recommended
Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine)
- ≥10 mg daily to keep vitamin B6 levels from decreasing across pregnancy
Vitamin B7 (Biotin)
- Prenatal supplements with ~100 mcg of biotin were recommended
- For women with bariatric surgery or major gastrointestinal problems, an extra 50—100 mcg of biotin may be needed
Vitamin B9 (folate)
- Prenatal supplements with ~400 mcg of folate were recommended
- It is recommended to start folate supplementation at conception or earlier to reduce the risk of neural tube defects (NTDs), small-for-gestational-age, and autism
Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin)
- It is recommended to have ~25 mcg daily preferably in the form of hydroxocobalamin for better absorption and retention (pending further research)
Choline
- Prenatal supplements with ≥350 mg of choline during the 1st and 2nd trimesters were recommended
- Prenatal supplements with ~600 mg of choline in the 3rd trimester, particularly for women who do not eat several eggs each week were recommended
DHA
- Prenatal supplements with ~600 mg of DHA were recommended, although more research is required
Inositol
- Prenatal supplements with ~500 mg of myo-inositol were recommended
- For women at risk of gestational diabetes or with previous NTDs, 4000 mg of inositol is recommended depending on diet
Link to the full article:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9275129/pdf/40748_2022_Article_139.pdf
Reference:
Adams JB et al. Evidence based recommendations for an optimal prenatal supplement for women in the US: vitamins and related nutrients. Matern Health Neonatol Perinatol. 2022;8(1):4.
Other articles that you might be interested in:
[Science Update] Maternal vitamin D supplementation during pregnancy and offspring’s risk of atopic eczema
WYE-EM-107-AUG-22
If you liked this post you may also like