![[Local data] The first city-wide iodine survey in Hong Kong](/sites/default/files/styles/header_image_article_mobile/public/2021-10/iodine-opt.jpg.webp?itok=HJgk_PBB)
Article
[Local data] The first city-wide iodine survey in Hong Kong
Public health
3 min read
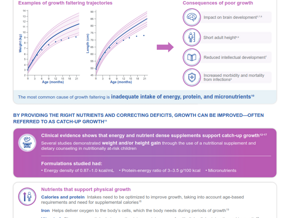
Questionnaire interviews and spot urine iodine tests were performed for all subjects whereas thyroid ultrasonography was done for school-aged children. Key findings are listed below:
- School-aged children
- Median urinary iodine concentration (UIC) was 115 mcg/L (classified as “adequate” iodine intake as per the cut-off points recommended in the WHO’s Guide)
- Total goitre rate assessed with body surface area-specific reference values and age-specific reference values (1.7% and 2.2% respectively) were within the category of “none” degree for iodine deficiency as per the prevalence of goitre by WHO
- Pregnant women
- Median UIC was 134 mcg/L (classified as “insufficient” iodine intake*)
- Median UIC of women taking iodine-containing supplements at an average daily iodine intake of at least 150 mcg/day was 156 mcg/L (classified as “adequate” iodine intake*)
- Lactating women
- Median UIC was 65 mcg/L (classified as “insufficient” iodine intake*)
- Median UIC of lactating women taking iodine-containing supplements at an average daily iodine intake of at least 150 mcg/day was 84 mcg/L (classified as “insufficient” iodine intake*)
* According to the WHO classification
Link to the full report:
https://www.chp.gov.hk/files/pdf/iodine_survey_report_en.pdf
WYE-EM-162-SEP-21
Reference
Hong Kong Department of Health. Iodine survey report. August 2021.
Other articles that you might be interested in:
[Local data] A local report on iodine status of pregnant women during early gestation
If you liked this post you may also like